ESD design guidelines in detail
The ESD design guidelines that we have developed (in conjunction with Tri Spatial Planning) draw on an extensive amount of research and existing practice, as well as information from our own experience. Our ideas come from many sources and it is significantly more comprehensive than any similar documents we are aware of.
See here for details of the philosophy behind these guidelines including a talk from our Principal at the 2019 Liveable Conference and other work with designing sustainable communities.
The final ESD Guidelines document includes a good number of sensible and innovative recommendations, broken down into the sections below:
Subdivision design and development
Subdivision dwellings
Buildings requiring a planning permit
Council buildings and assets
ESD guidelines: Subdivision design and development
Element 1 – Sequential development
- Recommendation 1.1 – Sequential development
Element 2 – Incorporation of relevant climate change, ESD, cultural heritage & ecological management reports
- [expand title=”Requirement 2.1 – Incorporation of relevant climate change and ESD reports” trigclass=”arrowright”]
 [/expand]
[/expand] - Requirement 2.2 – Cultural heritage assessments
- Requirement 2.3 – Ecological management
Element 3 – Subdivision design review
- [expand title=”Requirement 3.1 – Independent design review process” trigclass=”arrowright”]
 [/expand]
[/expand]
Element 4 – Urban Structure, connectivity and density
- Requirement 4.1 – Density and dwelling diversity
- Requirement 4.2 – Off-road personal transport highways
- Requirement 4.3 – Lot orientation
- Requirement 4.4 – Safe spaces (CPTED assessment)
- Requirement 4.5 – The street as a public space
Element 5 – Road reserve, path and park design and construction
- Requirement 5.1 – Sustainable materials
- Requirement 5.2 – Public open space
- [expand title=”Requirement 5.3 – Innovation Subdivision of 1000 Lots and greater” trigclass=”arrowright”]
 [/expand]
[/expand] - Requirement 5.4 – Energy efficient street lights and minimising light spill
Element 6 – Integrated water management, ecology, emissions sequestration and urban heat island effect
- Requirement 6.1 – Water Sensitive Urban Design (WSUD)
- [expand title=”Requirement 6.2 – Car parking design – for WSUD and urban ecology” trigclass=”arrowright”]
 [/expand]
[/expand] - Requirement 6.3 – Urban ecology
Element 7 – Waste
- Requirement 7.1 – Construction waste management
Element 8 – Innovation
- Requirement 8.1 – Demonstrate innovation for community benefit
Element 9 – Site and environmental management
- Requirement 9.1 – Site environmental management
Element 10 – Incorporation of ESD guidelines – Subdivisions dwellings (Housing ESD design guidelines)
- [expand title=”Requirement 10.1 – Incorporation of ESD guidelines – Subdivisions dwellings (Housing ESD design guidelines)” trigclass=”arrowright”]
 [/expand]
[/expand]
ESD guidelines: Subdivision dwellings 
Element 1 – Dwelling height
- Requirement 1.1 – Dwelling height
Element 2 – Accessible and adaptable dwellings
- [expand title=”Requirement 2.1 – Accessible and adaptable dwellings” trigclass=”arrowright”]
 [/expand]
[/expand] - Recommendation – Internal dependent persons unit
Element 3 – Thermal efficiency, reduced operation costs and reduced greenhouses gas emissions.
- Requirement 3.1 – Passive heating and cooling
- Recommendation – Ceiling fans
- Requirement 3.2 – Energy efficiency, greenhouse gas emissions and affordable living
- Requirement 3.3 – Renewable energy, greenhouse gas emissions and affordable living
Element 4 – Healthy environments for residents
- Requirement 4.1 – Healthy materials and finishes
- Requirement 4.2 – External noise
Element 5 – Healthy and inclusive communities.
- Requirement 5.1 – Public realm integration / activation of front yards
- Recommendation – Minimum front porch size
Element 6 – Water Sensitive Urban Design (WSUD).
- Requirement 6.1 – Water sensitive urban design, climate change resilience and waterway enhancement
Element 7 – To support ecological density and mitigate against the urban heat island effect
- [expand title=”Requirement 7.1 – Landscaping” trigclass=”arrowright”]
 [/expand]
[/expand] - [expand title=”Requirement 7.2 – Roof colour” trigclass=”arrowright”]
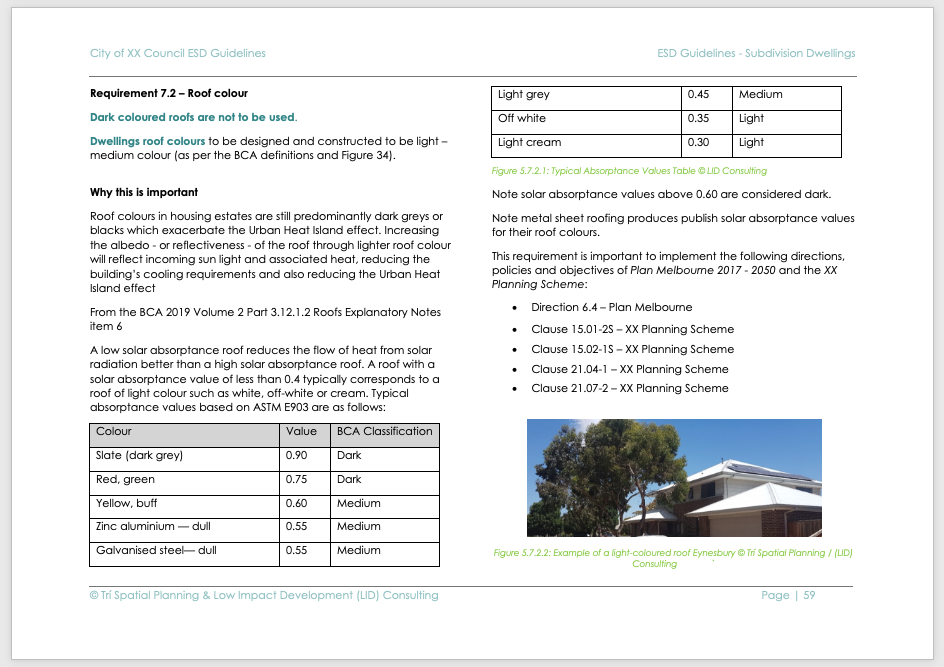 [/expand]
[/expand]
Element 8 – To increase potable water savings.
- Requirement 8.1 – Water efficient fixtures
- Requirement 8.2 – Water saving initiatives
Element 9 – Sustainable materials in dwelling design and landfill waste reduction.
- [expand title=”Requirement 9.1 – Sustainable materials” trigclass=”arrowright”]
 [/expand]
[/expand] - Requirement 9.2 – Construction waste
ESD guidelines: Buildings requiring a planning permit 
Background
Application
Objectives
Triggers and Application Requirements
- Trigger and application requirements – Table 6.4.1.1
- Innovation credits
- Passive design guide – residential / accommodation
- Passive design guide – non-residential
- Zero carbon emissions plan guide
- [expand title=”Aged care design guide” trigclass=”arrowright”]
 [/expand]
[/expand] - Service station design guide
- [expand title=”Car parking design guide” trigclass=”arrowright”]
 [/expand]
[/expand]
Council Buildings and assets 
Introduction and targets
Strategic alignment
Definition of ESD
[expand title=”Application and how to use these guidelines” trigclass=”arrowright”]  [/expand]
[/expand]
Objectives
Roles and responsibilities
Building and asset types triggers and ESD requirements
- All asset types
- Buildings
- Roads and infrastructure
- Stormwater
- Open Space
Supplementary and guidance information
- [expand title=”Consultant and contractors ESD experience” trigclass=”arrowright”]
 [/expand]
[/expand] - Sustainable materials from the Infrastructure Design Manual (IDM) Sustainable Infrastructure Guidelines (SIG)
- Passive design statement
- Zero carbon emissions plan guide
- Building users guide
- Sustainability management plan
- ESD and the capital works cycle


