Sustainable dwelling design
Early stage design decisions are the best way to achieve sustainable buildings at lower cost.
Whether you’re building your own home, developing multi-unit apartments or designing new communities, use these sustainable house design tips to factor sustainability in early, saving time, money and the planet.
1 Windows Performance
Single glazed aluminium windows generally achieve R0.17 and the best available thermally broken double glazed aluminium windows with low e glass can be three times better at R0.5 (European style triple glazed windows can get better again). Be selective with window sizes and location. Windows performance is discussed in U values (the rate of heat transfer through a window) which are the reciprocal value of the R value (the resistance to heat transfer) i.e. 1/0.17 gives a U value of 5.8 and 1/0.5 gives a U value of 2. A lower U value is preferable as this represents less heat transfer through the window.

Be selective with window size, location and material for best performance

Small gaps let a lot of heat out. Picture source: http://premierinsulation.com.au/wall-insulation-adelaide/
Walls generally have R2.0-3.0 insulation value to ensure a reasonable energy rating. Bearing in mind the window R values described in 1 above, windows are typically in the order of 1/10th – 1/6th as good at insulating as walls. Avoid numerous excessively large windows. Also ensure insulation is installed correctly and gaps around plumbing/air-conditioning pipe penetrations and cabling are sealed. Heat travels through gaps like noise does – so a small gap can let a lot of heat in or out. Try to avoid placing power points or similar wall penetrations on the external wall of a dwelling, as this often leads to gaps in insulation batts where electricians remove insulation so it doesn’t sit up against the back of their power points.
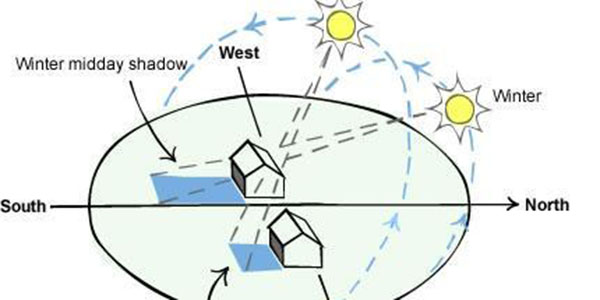
External shading is significantly more effective at keeping heat out than internal blinds. External adjustable vertical shading can be effective where balconies provide access to adjust the blinds. Blinds incorporated in the leading edge of the eave or balcony above are a very easy to access and use shading solution. This vertical shading is the most effective for east and west facing windows. Horizontal shading can be effective for north facing windows as, if designed with an appropriate projection distance, it should keep out summer sun while admitting lower level winter sun. Ensure fixed shading does not permanently restrict winter sun ingress, as this can negatively impact the energy rating.
Window tinting is common in commercial building where shading is not incorporated. Simple window tinting should be avoided always on south elevations, and generally avoided on other elevations with adjustable shading preferred, as tinting keeps out desirable winter passive heat gains and reduces daylight, as well as less desirable summer heat. More advanced (and expensive) low e glasses can reduce heat ingress and maintain good daylight transmission levels.
A concrete slab typically provides approximately R0.15 insulation value – very little insulation. The total star energy rating of apartments sitting on a suspended concrete slab above a carpark, can be improved by R0.5 – R1.0 by adding R1.0 – R1.5 insulation to the underside of this slab. Remember to insulate under floors where there is a non conditioned (heated or cooled) space below. Insulation can be reflective polystyrene board, firmer bulk insulation blanket, rigid board or spray on solutions.
Ensure all windows have a substantial openable component and ideally windows on multiple facades to allow good, direct breeze paths for natural cooling. The cooling effect is even better where window openings are are between 700 – 1700mm ie at the height to blow directly across our bodies when occupying a room. A good breeze will create the feeling of a 2-5 degree temperature reduction. Ceiling fans have the same impact and are effective in bedrooms at all temperatures and living spaces for all but the hottest days. Running ceiling fans reduce the days when air-conditioning needs to be considered – generating significant energy use savings.
Include a drying rail in laundries or European laundry cupboards. This can be as simple as a single robe type hanging rail. Hanging clothes on coat hangers or underwear peg wheels on this rail allows simple passive drying of clothes and removes the need for a power consuming electric clothes dryer. Fit the rail 2150mm above floor level and it can be reached by most people, while still fitting a clothes dryer underneath if the occupants really want this.
Gas is a fossil fuel that generates carbon (dioxide) emissions when burnt. Electricity can be supplied by burning fossil fuels or from renewable sources such as solar PV panel systems or wind. Space heating and cooling, and hot water generation represent 77% of the energy consumption in Victorian homes and cooking a further 3% (1). By replacing gas appliances with electric appliances dwellings can become zero emissions in terms of the energy consumed within the home. Making this change is the simple way for residents in new dwellings to slash their carbon emissions. Further electricity prices are now falling due to the influx of renewables in our mains grid, and electric appliances that use heat pump technology (water heaters and reverse cycle air-conditioning units) are more efficient than gas equivalent appliances.
(1) Paul Ryan and Alan Pears, ‘Unravelling Home Energy Use across Australia – Renew’, Renew, 23 May 2019, https://renew.org.au/renew-magazine/efficient-homes/unravelling-home-energy-use-across-australia/.
- Water saving solutions – efficient fixtures and water tanks
- Water Sensitive Urban Design which considers the quality of water leaving a site and entering our drains, creeks and the bay,
- Selection of more environmentally friendly material choices,
- With better sealed buildings, ensuring off-gassing from modern materials is minimised is now more important,
- Waste minimisation during demolition, construction and facilities and planning to ensure similar during operation
- Designing to more simply facilitate alternative transport options to car use
- Maintaining and enhancing the urban ecology
- Community building design ideas and Innovation